Dev C++ Using Switch
Sometimes when creating a C++ program, you run into a situation in which you want to compare one thing to a number of other things. Let's say, for example, that you took a character from the user and wanted to compare this to a number of characters to perform different actions. For now, let's just say that you have three commands which operate from the keys: 'h', 'e', and 'q'.
Jun 03, 2015 Write a C program to print day of week name using switch case. Write a C program print total number of days in a month using switch case. Write a C program to check whether an alphabet is vowel or consonant using switch case. Write a C program to find maximum between two numbers using switch case. Nov 29, 2016 You can get visibility into the health and performance of your Cisco ASA environment in a single dashboard. View VPN tunnel status and get help monitoring firewall high availability, health, and readiness. It’s also designed to automatically discover and filter with ACLs, show rule hit counts, and detect shadow and redundant rules.
May 12, 2017 Switch Statement in C/C Switch case statements are a substitute for long if statements that compare a variable to several integral values The switch statement is a multiway branch statement. Jun 03, 2015 Write a C program to input an alphabet and check vowel or consonant using switch case. Logic to check vowel or consonant using switch case in C programming. Learn C programming, Data Structures tutorials, exercises, examples, programs, hacks, tips and tricks online. Jun 03, 2015 switch case is a branching statement used to perform action based on available choices, instead of making decisions based on conditions. Using switch case you can write more clean and optimal code than if else statement. Switch case only works with integer, character and enumeration constants. In this exercises we will focus on the use of switch case statement. If c is not an a or A, the default statement is executed. Visual Studio 2017 and later: (available with /std:c17) The fallthrough attribute is specified in the C17 standard. It can be used in a switch statement as a hint to the compiler (or to anyone reading the code) that fall-through behavior is intended.
We can use an if-statement to check equality to 'h', 'e', and 'q' - remember that we use single quotes because we're dealing with chars, not strings. So let's just write the code in the way we're used to (and let's wrap a while loop around it so it keeps getting a character and acting upon what it was, because that makes our program slightly better and easier to test), using if-statements, like the following:
This program should be something you're comfortable with creating by this point, however your programmer instincts should also be kicking in and telling you that you shouldn't be repeating so much code here. One of the core principles of object orientated programming is DRY: Don't Repeat Yourself. In this program we're having to repeat a lot of code for the 'else if's including using ch every time we're doing a comparison.
The solution to this 'problem' is what this tutorial is all about: switch statements. These are essentially just a really nice way to compare one expression to a bunch of different things. They are started via the switch keyword, and from there comparisons are made using a case: syntax. It isn't easily described in words, so take a look at the syntax below:
The different cases essentially act as many if/else-ifs in a chain, and an 'else' type clause can be specified by using default:
This type of functionality should be reasonably easy to understand with if-statements securely under your belt, and so if you're feeling brave - try porting the basic program we created at the start of this tutorial to use if-statements. If you're not quite that brave, the cleaner and neater switch version of the code is below:
Switch case statement is used when we have multiple conditions and we need to perform different action based on the condition. When we have multiple conditions and we need to execute a block of statements when a particular condition is satisfied. In such case either we can use lengthy if.else-if statement or switch case. The problem with lengthy if.else-if is that it becomes complex when we have several conditions. The switch case is a clean and efficient method of handling such scenarios.
Switch Dev Menu
The syntax of Switch case statement:
Failed update error 1 itunes 3utools. Check all connections, also try to change the battery;Faulty baseband flash or processor;Happens frequently after water damage. Remove and clean motherboard;H.Error 26Baseband/CPU/Chip. H.Error 23In software you have to set a default web browser;In hardware, it's a communication problem. H.Error 27Chip data does not match, please use the chip instrument to fix the chip.Error 28CPU or hard disk.
Switch Case statement is mostly used with break statement even though the break statement is optional. We will first see an example without break statement and then we will discuss switch case with break
Example of Switch Case
Output:
Explanation: In switch I gave an expression, you can give variable as well. I gave the expression num+2, where num value is 5 and after addition the expression resulted 7. Since there is no case defined with value 4 the default case got executed.
Switch Case Flow Diagram
It evaluates the value of expression or variable (based on whatever is given inside switch braces), then based on the outcome it executes the corresponding case.
Break statement in Switch Case

Before we discuss about break statement, Let’s see what happens when we don’t use break statement in switch case. See the example below:
Output:
In the above program, we have the variable i inside switch braces, which means whatever the value of variable i is, the corresponding case block gets executed. We have passed integer value 2 to the switch, so the control switched to the case 2, however we don’t have break statement after the case 2 that caused the flow to continue to the subsequent cases till the end. However this is not what we wanted, we wanted to execute the right case block and ignore rest blocks. The solution to this issue is to use the break statement in after every case block.
Break statements are used when you want your program-flow to come out of the switch body. Whenever a break statement is encountered in the switch body, the execution flow would directly come out of the switch, ignoring rest of the cases. This is why you must end each case block with the break statement.
Let’s take the same example but this time with break statement.
Output:
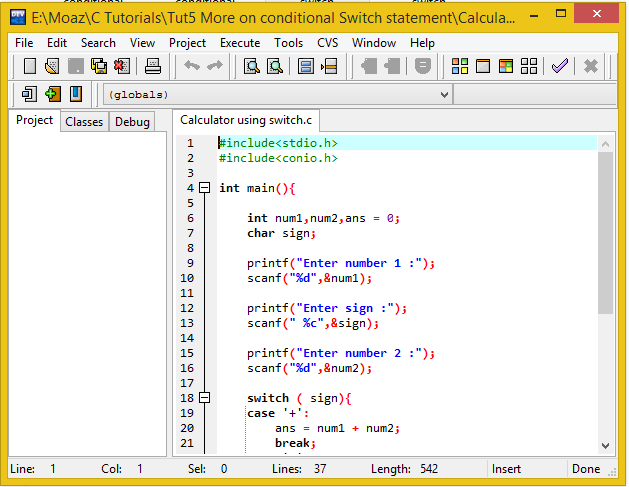
Dev C++ Programs
Now you can see that only case 2 got executed, rest of the subsequent cases were ignored.
Why didn’t I use break statement after default?
The control would itself come out of the switch after default so I didn’t use break statement after it, however if you want you can use it, there is no harm in doing that.
Important Notes
1) Case doesn’t always need to have order 1, 2, 3 and so on. It can have any integer value after case keyword. Also, case doesn’t need to be in an ascending order always, you can specify them in any order based on the requirement.
Dev C Using Switch Download
2) You can also use characters in switch case. for example –
Dev C++ Using Switch Number
3) Nesting of switch statements are allowed, which means you can have switch statements inside another switch. However nested switch statements should be avoided as it makes program more complex and less readable.